TCP Connection Methods
TCP Header Structure
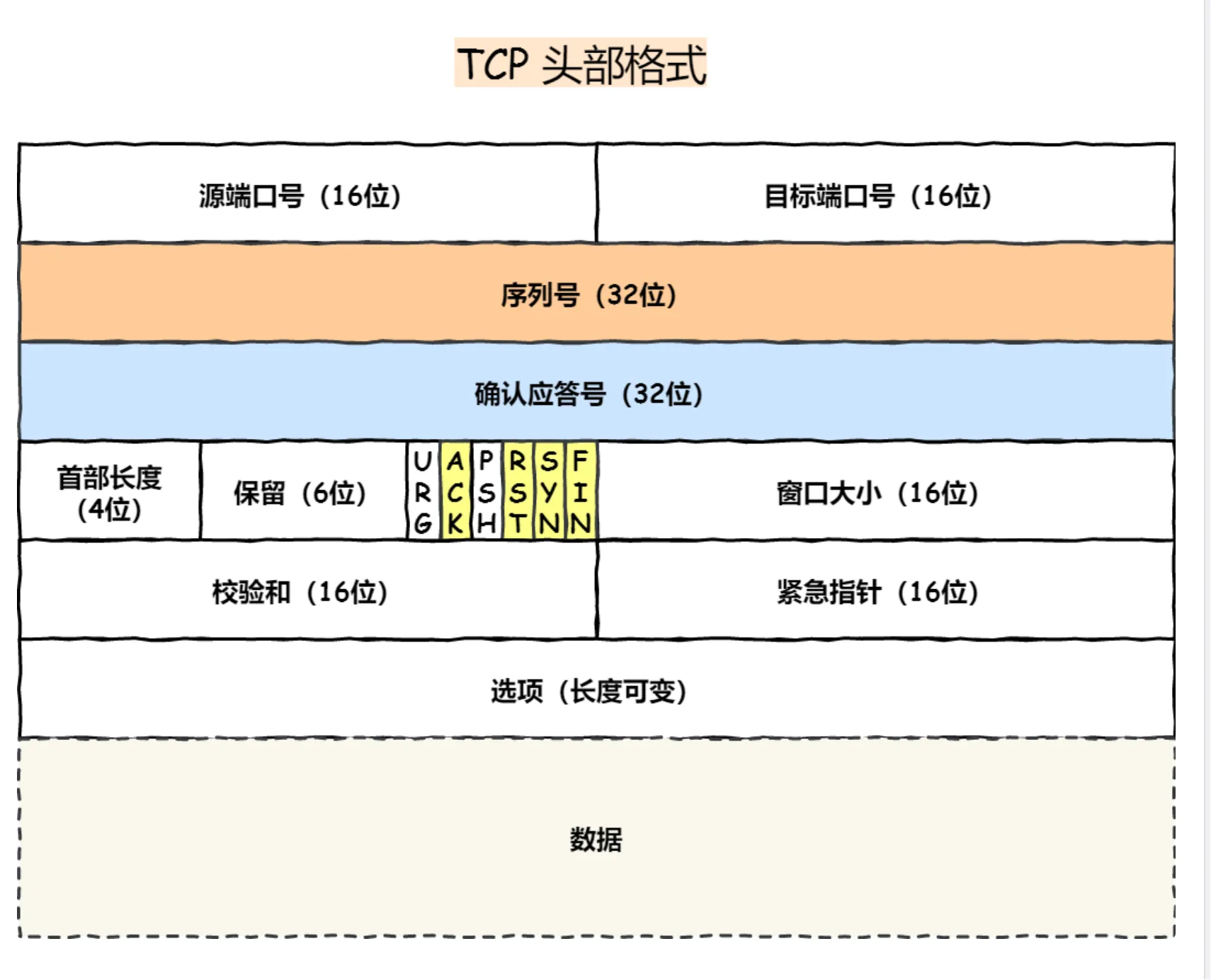 Control Bits:
Control Bits:
- SYN: Indicates the desire to establish a connection and sets the initial sequence number in the “Sequence Number” field.
- ACK: Acknowledgment bit, TCP specifies that this bit must be set to 1 except for the SYN packet used to establish the connection, which is used to confirm the receipt of data.
- RST: Indicates that an abnormal situation has occurred in the TCP connection and the connection must be forcibly disconnected.
- FIN: When the communication ends and the connection is to be disconnected, both hosts can exchange TCP segments with the FIN bit set to 1.
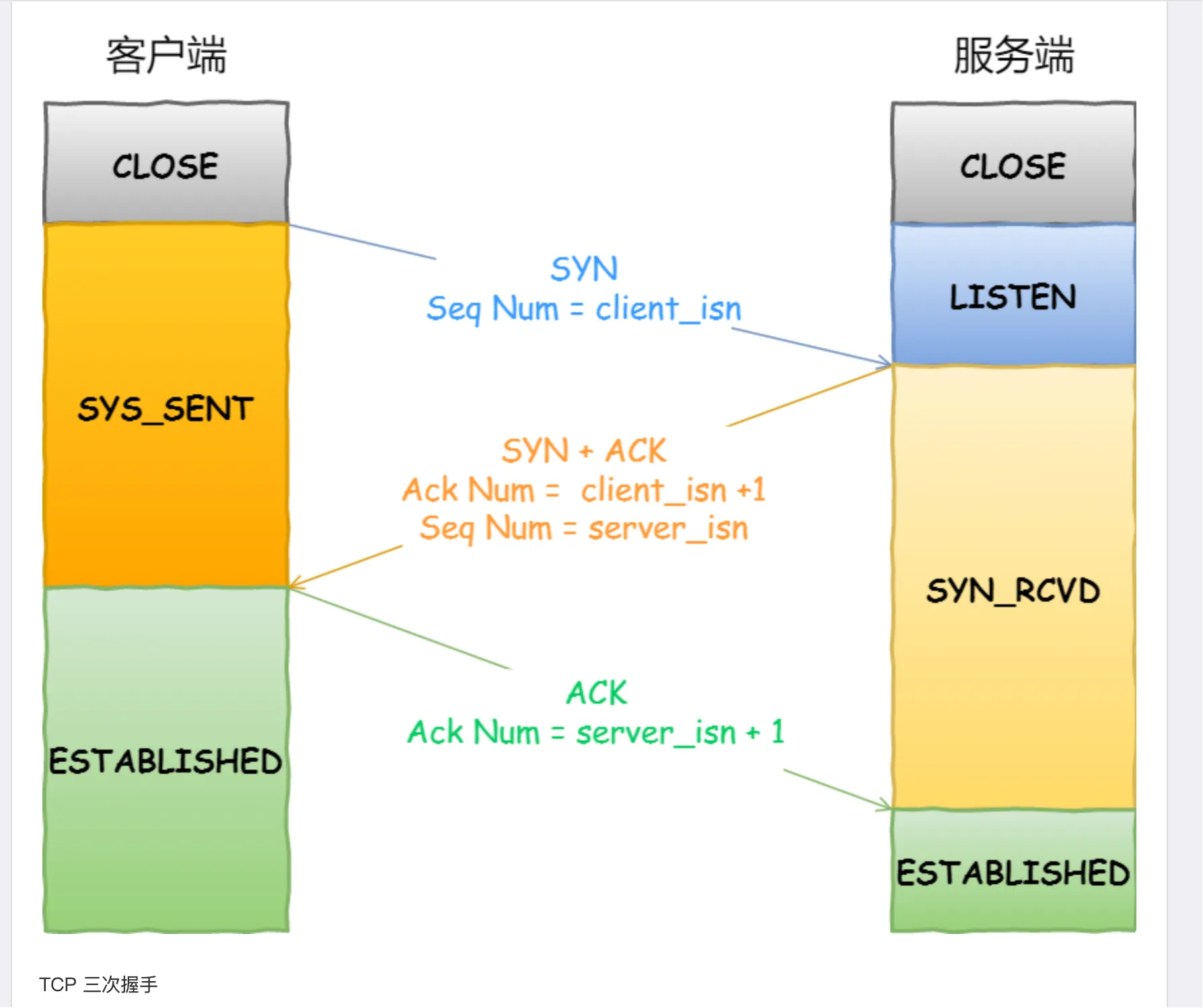
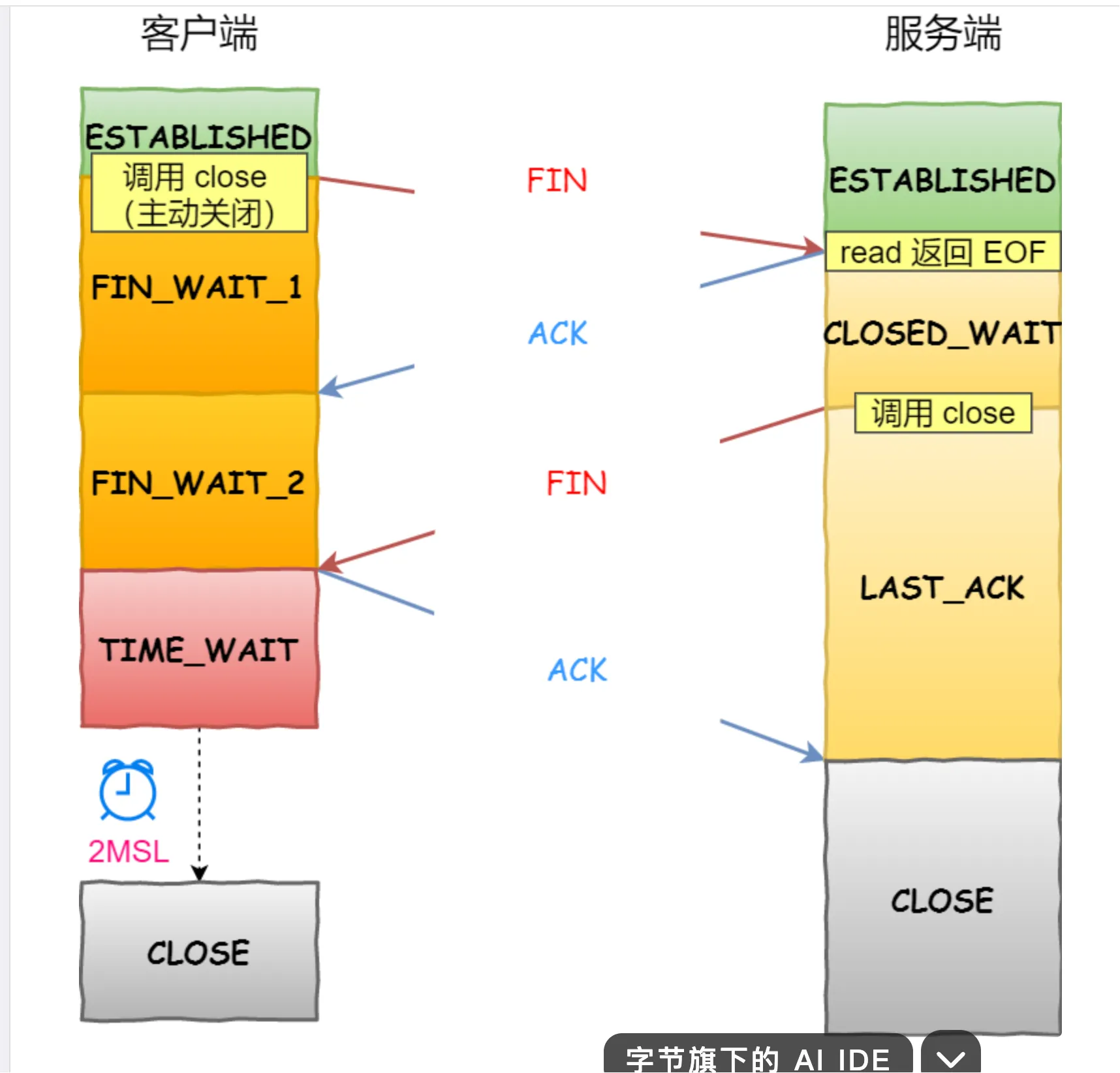
The state transition of the TCP client revolves around the three stages of “connection establishment - data transmission - connection closure,” with the core states including: CLOSED → SYN-SENT → ESTABLISHED → FIN-WAIT-1 → FIN-WAIT-2 → TIME-WAIT → CLOSED (active closure process).
The typical state transition of the server is: CLOSED → LISTEN → SYN-RECEIVED → ESTABLISHED (connection establishment); if passively closed: ESTABLISHED → CLOSE-WAIT → LAST-ACK → CLOSED.
Difference between 502 and 504
- 502 Gateway Error: Usually occurs when the backend service returns an invalid response (such as returning HTML instead of JSON).
- 504 Gateway Timeout: Usually occurs when the backend service response time exceeds the gateway timeout time.
Common Network Commands
- ping: Tests the network connection between hosts.
- traceroute: Traces the path of data packets from the source host to the target host.
- netstat: Displays network connections, routing table, and interface statistics.
- tcpdump: Captures and analyzes network traffic.
- wget: Downloads files from the network.
- curl: Sends HTTP requests and displays responses.
- ifconfig/ip: Configures and displays network interface information.
- route: Displays and operates the IP routing table.
- dig: Queries DNS servers.
- nslookup: Queries DNS servers.
- host: Queries DNS servers.
- whois: Queries domain registration information.
- nmap: Network scanning tool.
- iperf: Tests network bandwidth.
- tcpdump: Captures and analyzes network traffic.
How to View the Process ID of the 80 Port
- View process ID:
netstat -tuln | grep :80 - View process details:
ps -ef | grep <pid>
What Have You Done for Stability?
Open question
